MR3 Unleashes Hive on Kubernetes

Organizations that want to take advantage of the latest capabilities in Apache Hive but don’t want to deal with painful Hadoop upgrades or difficult LLAP configurations have another option in the form of MR3, a new execution engine for Hive that runs natively on Hadoop and Kubernetes.
MR3 is a software product developed by a team led by Sungwoo Park. The software, which is not open source, is sold by a Delaware-based software company called DataMonad. After prototyping a Java-based execution engine called MR2 in the 2013 timeframe, development of Scala-based MR3 began in 2015. The first release of MR3 was delivered in early 2018, and version 1.0 was released yesterday.
According to DataMonad, MR3 is an execution engine for big data processing, and Hive is the first and main application that’s been configured to run on it (Tez is also supported). The company says MR3 offers comparable performance to the latest release of Hive, dubbed LLAP, but without the technical complexity.
The company has shared results of benchmark tests on its blog that show Hive running on MR3 running neck-and-neck with Hive LLAP on a Hortonworks cluster. The same test shows Hive/MR3 outperforming by a wide margin Presto and Spark SQL, two other competing SQL data warehousing solutions that run on Hadoop and emerging cloud platforms.
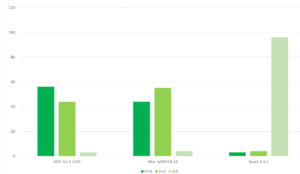
Hive LLAP had slightly more first-place finishes on the TPC-DS test than Hive on MR3 (Image source: DataMonad)
“In our evaluation based on the TPC-DS benchmark with a scale factor of 10 terabytes, Hive on MR3 runs about three times faster than Presto and about four times faster than SparkSQL with respect to the geometric mean of execution times,” the company states in the FAQ section of its website.
While momentum behind Hadoop has waned, Hive continues to be one of the most popular of the Hadoop sub-projects, as organizations either maintain their existing Hadoop clusters or seek cheaper and more open alternatives to other data warehouse systems.
Hive, which was originally developed to run atop Hadoop clusters at Facebook, has stuck around, despite the emergence of Presto, which also was developed at Facebook specifically to replace Hive. The open source software has also withstood competition from Impala, which was Cloudera’s response to Hive, as well as SparkSQL, which has grown in popularity as Apache Spark usage has taken off.
MR3 fully replaces MapReduce atop Hadoop clusters, where it runs atop YARN. Customers can “easily switch between different versions of Hive without upgrading Hadoop,” the company says. That means that all major versions of Hive, from Hive 1 to Hive 4, can run in the same cluster and users can use them as needed.
But MR3 also natively supports Kubernetes, which is widely viewed as the resource scheduler that will replace YARN as in the emerging big data cloud stack. DataMonad says MR3 will manage all the worker pods associated with a Kubernetes cluster. It also supports enterprise features such as high availability, Kerberos authentication, encryption, and integration with Apache Ranger. There are limitations to the amount of memory that an MR3 on Kubernetes cluster can handle, compared to the Hadoop version, however.
Customers can purchase a license to use MR3 from DataMonad at a cost of $24,528 per TB per year. The company says that’s equivalent to paying $0.35 per hour for a node with 128GB of memory, which is cheaper than Presto, Cloudera Data Warehouse, and Hive, it says.
Related Items:
Building Presto Business No Magic Trick for Starburst
Hadoop Engines Compete in Comcast Query ‘Smackdown’
Microsoft Expands Hadoop on Azure
Editor’s note: This article was corrected. Sungwoo Park was not the founder of DataMonad. Datanami regrets the error.