TigerGraph Releases New Benchmark Report

TigerGraph has released a new benchmark report for its graph analytics software. The company used the Data Benchmark Council (LDBC) Social Network Benchmark (SNB) Scale Factor 30k dataset. The results show that TigerGraph can run deep-link OLAP style queries on 36TB of raw data with 73 billion vertices and 534 billion edges, “returning results on data-intensive queries in a few minutes or less.”
The LDBC SNB benchmark is a testing methodology used to confirm a graph platform’s performance. TigerGraph claims this benchmark study is, “as far as we can ascertain, the first time a graph database has been tested at this scale,” and it “clearly demonstrates TigerGraph’s ability to handle a big graph workload in a real production environment, where tens of terabytes of connected data with hourly or daily incremental updates is the norm.”
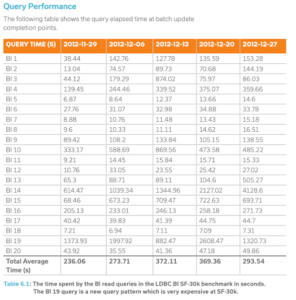
The benchmark testing was carried out with a cluster 40 Google Cloud Platform machines used with the 30k dataset for business analytics workloads, measuring “loading time, storage size, and query latency for 20 BI queries,” according to a company blog post. The virtual machines were used with the m1-ultraman-40 instance on CentOS Linux 7. TigerGraph’s own query language, GSQL, was used for implementation, and the study says that “queries were compiled and loaded into the database as stored procedures.”
The company appears passionate about benchmarking. In a recent blog post featuring a scathing review of a competitor’s benchmark methods, TigerGraph’s VP of Engineering, Dr. Mingxi Wu, explains how “a benchmark evaluates alternative products based on well-defined objective criteria spanning multiple dimensions. It allows one to quantitatively compare different technologies to make more objective choices for their software purchases.”
Wu also gives a detailed explanation of why he prefers using the LDBC SNB benchmark methodology, including its ability to simulate realistic data within its data set with multiple vertex and edge types, its ability to use any query language, and its capacity for representative graph queries covering different choke points.
The new report also features cross validation details and results, along with full technical details of the benchmark testing, including hardware, storage, and networking specifics. Scripts used for the benchmark are available on GitHub.
The study concludes with the assertion that “No other graph database vendor or relational database vendor has demonstrated equivalent analytical and operational capabilities on this large scale updatable graph to the best of our knowledge.”
Read the whitepaper containing the full report here.
Related Items:
A Million Dollars Up for Grabs in TigerGraph Challenge