(Jurik Peter/Shutterstock)
Yahoo today announced that it’s open sourcing Pulsar, a new distributed “publish and subscribe” messaging systems designed to be highly scalable while maintaining low levels of latency. The bus already backs some of Yahoo’s key apps, and now the Web giant is seeking the help of the open source community to take Pulsar to the next level.
In a post to the Yahoo Engineering blog, Yahoo developers Joe Francis and Matteo Merli explained the application requirements that spurred the creation of the new “pub-sub” messaging system that would become Pulsar.
“These applications provide real-time services, and need publish-latencies of 5ms on average and no more than 15ms at the 99th percentile,” they write. “At Internet scale, these applications require a messaging system with ordering, strong durability, and delivery guarantees.” The messages must also be committed to multiple disks or nodes in order to get to the 99.999% guaranteed durability level, they add.
“At the time we started, we could not find any existing open-source messaging solution that could provide the scale, performance, and features Yahoo required to provide messaging as a hosted service, supporting a million topics,” Francis and Merli write. “So we set out to build Pulsar as a general messaging solution, that also addresses these specific requirements.”
Yahoo designed Pulsar to scale horizontally on commodity hardware, and to provide messaging as a service to multiple applications. The system can scale to handle millions of independent topics and millions of messages published per second, according to Pulsar’s GitHub page.
Developers and administrators interact with Pulsar through a collection of APIs. The software also includes a client library that encapsulates the messaging protocol and handles “complex” functions like service discovery and establishing and recovering connections.
Pulsar Architecture
A Pulsar cluster is composed of a set of brokers, BookKeepers (or bookies), and ZooKeeper for coordination and configuration management. A Pulsar instance typically consists of multiple physical clusters that are geographically separated from one another, Yahoo says.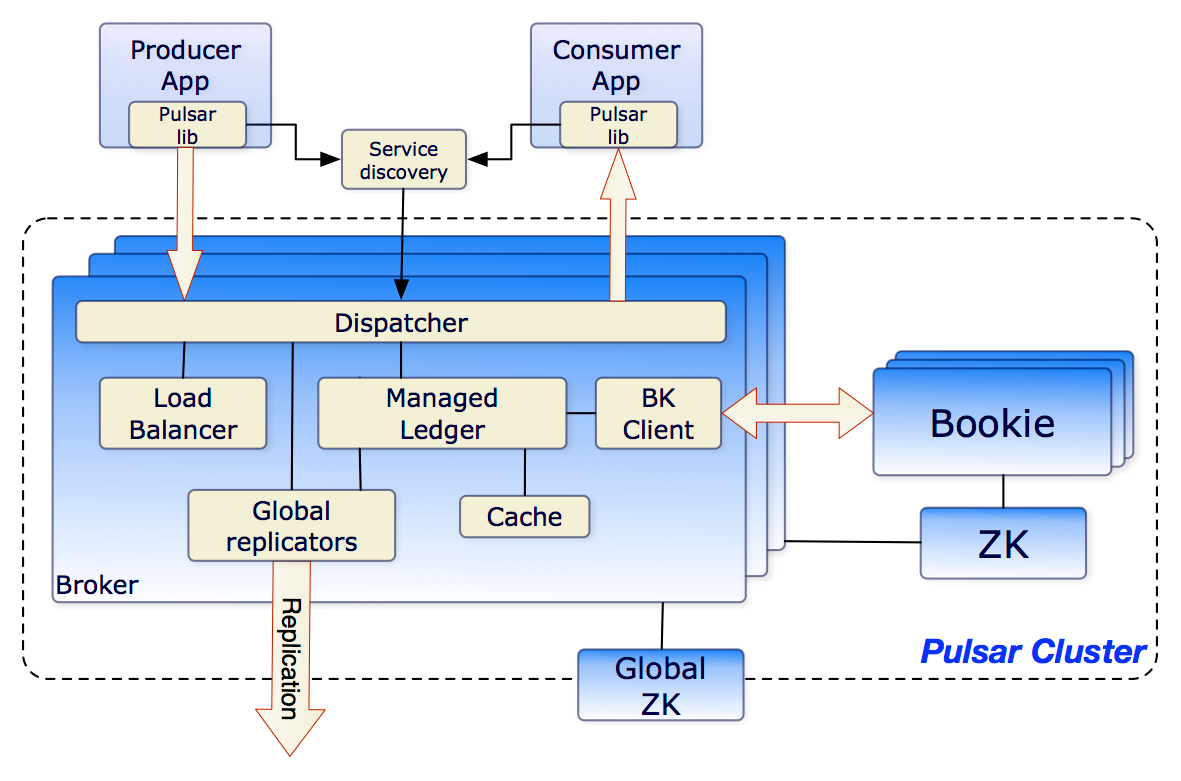
Pulsar uses Apache Bookkeeper (committed by Yahoo to open source in 2011) as its durable storage mechanism. “With Bookkeeper, applications can create many independent logs, called ledgers,” Pulsar’s project page on GitHub says. “A ledger is an append-only data structure with a single writer that is assigned to multiple storage nodes (or bookies) and whose entries are replicated to multiple of these nodes.”
Pulsar uses brokers to serve topics. Each topic is assigned to a broker, and an individual broker can serve thousands of topics, Yahoo says. “The broker accepts messages from writers, commits them to a durable store, and dispatches them to readers,” Yahoo says.
An instance of Apache Zookeeper keeps all the other pieces of Pulsar working together. Yahoo contributed ZooKeeper to the Apache Software Foundation in 2008, and since then the software has become a key component of Apache Hadoop and other big data frameworks.
It appears the use of BookKeeper is key to Pulsar’s high level of durability, and the capability to scale elements of the messaging bus independently. It also offers clues as to why Yahoo developed Pulsar in the first place, and didn’t rely on other open source messaging systems, such as Apache Kafka.
“By using separate physical disks (one for journal and another for general storage), bookies are able to isolate the effects of read operations from impacting the latency of ongoing write operations, and vice-versa,” the Yahoo developers write on their blog. “Since read and write paths are decoupled, spikes in reads – which commonly occur when readers drain backlog to catch up – do not impact publish latencies in Pulsar. This sets Pulsar apart from other commonly-used messaging systems.”
While Kafka was available when Yahoo started developing Pulsar, the technology didn’t offer some of the features that Yahoo’s engineering team required, Yahoo tells Datanami.
Specifically, features like offset (cursor) management, geo-replication, multi-tenancy, and performance under message backlog conditions were not available in Kafka then, and some even aren’t available now, a Yahoo spokesperson says.
Yahoo’s engineering team deployed its first Pulsar instance in the spring of 2015, and use of it has grown quickly since then. Today Pulsar backs Yahoo applications like Mail, Finance, Sports, Gemini Ads, and Sherpa, which is Yahoo’s distributed key-value service. All told, Pulsar publishes more than 100 billion messages per day across 1.4 million topics with an average latency of less than 5 ms.
By making Pulsar available under an Apache 2.0 license, Yahoo hopes to spur development of the messaging bus. Specific areas the company is currently looking to improve upon include decreasing the tiem it takes to migrate tpics among brokers from 10 seconds to less than one second, improving the 99.9-percentile publish latencies to 5ms, and providing additional language bindings for Pulsar.
Yahoo’s Pulsar project is not to be confused with the real-time analytics platform named Pulsar that came out eBay. You can read more about the eBay Software Foundation’s product at gopulsar.io.
April 18, 2024
- SAS Viya Expands Generative AI Capabilities with New Data Maker and Industry-Specific Assistants
- Moveworks Partners with Microsoft to Deliver Secure, Scalable Generative AI Solutions to Customers
- Rockset Announces 2024 Index Conference, Industry Event for Engineers Building Search, Analytics, and AI Applications at Scale
- SAS Advances Industry Solutions with Packaged AI Models
- Altair Acquires Cambridge Semantics, Powering Next-Gen Enterprise Data Fabrics and GenAI
- SAS Adds to Its Trustworthy AI Offerings with Model Cards and AI Governance Services
- Fujitsu and Oracle Collaborate to Deliver Sovereign Cloud and AI Capabilities in Japan
- Kore.ai Introduces Experience Optimization Platform V11.0, Accelerating AI Deployment
- Volumez Expands Collaboration with AWS, Joins ISV Accelerate Program
- AI Squared Raises $13.8M to Accelerate Widespread AI Adoption Within Organizations
- Hazelcast Sets New Standards for AI Workloads with Platform 5.4 Enhancements
April 17, 2024
- Immuta Launches Domains Policy Enforcement Capability to Simplify Enterprise-wide Data Security and Governance
- ThoughtSpot Makes Embedding AI-Powered Analytics Easy and Ubiquitous for Everyone
- Cribl Ushers in a New Era of Data Storage Simplicity with Cribl Lake
- Neo4j Welcomes New GQL International Standard in Major Milestone for Database Industry
- General Assembly Report: Tech Firms Pay Top Dollar to Secure Competent AI Professionals
- Appen Named a Leader in Everest Group’s Data Annotation and Labeling Solutions for AI/ML PEAK Matrix Assessment 2024
- Loft Labs Raises $24M in Series A Funding to Enhance Multi-Cloud and AI Infrastructure Capabilities
- Hitachi Vantara Unveils Virtual Storage Platform One, Providing the Data Foundation for Unified Hybrid Cloud Storage
April 16, 2024
Most Read Features
Sorry. No data so far.
Most Read News In Brief
Sorry. No data so far.
Most Read This Just In
Sorry. No data so far.
Sponsored Partner Content
-
Get your Data AI Ready – Celebrate One Year of Deep Dish Data Virtual Series!
-
Supercharge Your Data Lake with Spark 3.3
-
Learn How to Build a Custom Chatbot Using a RAG Workflow in Minutes [Hands-on Demo]
-
Overcome ETL Bottlenecks with Metadata-driven Integration for the AI Era [Free Guide]
-
Gartner® Hype Cycle™ for Analytics and Business Intelligence 2023
-
The Art of Mastering Data Quality for AI and Analytics
Sponsored Whitepapers
Contributors
Featured Events
-
Call & Contact Center Expo
 April 24 - April 25Las Vegas NV United States
April 24 - April 25Las Vegas NV United States -
AI & Big Data Expo North America 2024
 June 5 - June 6Santa Clara CA United States
June 5 - June 6Santa Clara CA United States -
AI Hardware & Edge AI Summit 2024
 September 10 - September 12San Jose CA United States
September 10 - September 12San Jose CA United States -
CDAO Government 2024
 September 18 - September 19Washington DC United States
September 18 - September 19Washington DC United States